
The Department of Surgery at the American University of Beirut Medical Center (AUBMC) performed the first Endoscopic Endonasal resection of superior orbital fissure and optic canal tumor in Lebanon. This advanced approach helped save the life of a 5 year-old girl who presented to the Medical Center with a case of optic nerve tumor extending to the superior orbital fissure. The first- of-its-kind procedure allows the surgeon to remove tumors in the brain and at the top of the spine without the need for large incisions or without having to remove parts of the skull, making recovery quicker and less painful.
The surgery was performed by Dr. Houssein Darwish, Brain and Spine Surgeon, Division of Neurosurgery, Department of Surgery at AUBMC assisted by Ear, Nose and Throat (ENT) Dr. Zeina Korban and Dr. Osama Hadi. The tumor was pushing on the young patient’s optic nerve and deteriorating her vision to the extent of blindness. These kinds of tumors, skull base tumors, used to be approached previously through a major craniotomy (open brain surgery). Using this novel approach for the first time in Lebanon, the team resected the lesion without resorting to opening the child’s skull and brain by only using her nose and an endoscope.
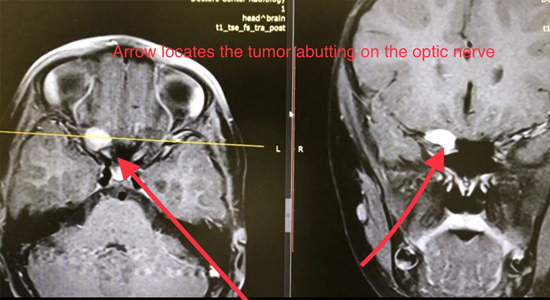
The child recovered within two days and was discharged from the Medical Center accordingly. Two weeks after surgery the child reported seeing shades of light.
“The surgery is a major advancement in skull base tumor resection. At AUBMC, we are taking the skull base surgery to the next advanced level where we can go to areas that were considered to be very difficult to approach unless a major open brain surgery is performed,” said Dr. Houssein Darwish. “This technique provides us with the ability to tackle brain and neural tissue tumors without touching the brain till the end of the resection. Thanks to this new approach, we can promise patients to have faster recovery and less morbidity,” added Dr. Darwish.
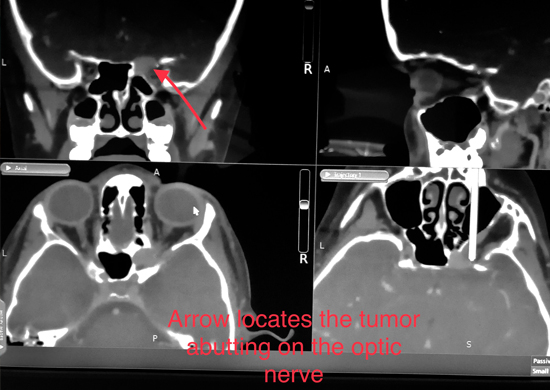
Endoscopic endo-nasal skull base surgery is a minimally invasive technique that allows a surgeon to go through the nose to operate on areas at the front of the brain and the cervical spine. A thin tube called an endoscope is thread through the nose and sinuses. This gives the surgeon access to parts of the patient’s brain that would be hard to reach using traditional surgical approaches and often require large incisions and removal of parts of the skull [1]. Endoscopic endo-nasal optic nerve surgery is an effective and minimally invasive technique affording the restoration of visual function in patients with non-traumatic compressive processes of the orbital apex and optic nerve. The timing of decompression remains crucial, and patients should undergo such a procedure early in the disease course before optic atrophy.
The endoscope has been previously used to resect pituitary tumors, whereas through this approach, the boundaries of tumor resection are extended without opening the brain and the skull, which ultimately leads to faster recovery and less morbidity.